CELL TO STACK: THE MISSING LINK IN PEM ELECTROLYSIS
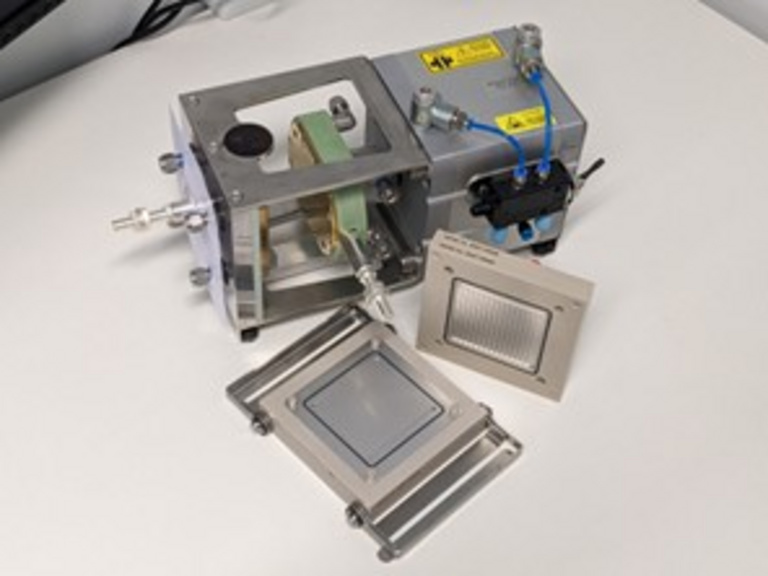
As part of the HyGen subproject focusing on the improvement of PEM electrolysis, a direct, systematic comparison between single-cell and stack tests was carried out for the first time. Identical cell materials (catalyst-coated membrane, porous transport layers, gas diffusion layer) and identical test protocols were used for this purpose. The aim was to verify the transferability of results from single cells to stacks, thereby accelerating future development processes, making them more precise and reducing costs.
Since single cells can be tested much more quickly and flexibly, they often form the basis for technological decisions. However, reliable transferability to stacks has only been proven to a limited extent. There was a lack of reliable comparative data for evaluating degradation, especially under dynamic operating conditions. This is exactly where the project comes in.
Impact and effects
Taking certain parameters into account, the investigations showed a high degree of comparability between single-cell and stack results under certain conditions. This means that in future, development can focus on the single-cell level at an earlier stage, resulting in considerable time and cost savings. Simultaneous tests revealed that degradation mechanisms occur largely independently of the test bench level. The test protocols and measurements established in the project enable precise characterisation and play a central role in result validation. The knowledge generated strengthens the basis for scalable, robust PEM technologies and increases reliability for industrial applications.
Highlights
• Taking certain conditions into account, results from the single-cell level can be transferred to stacks.
• Characterisation using EIS has been successfully established at the stack level and used in a comparable manner to single cells.
• Single-cell tests offer flexibility and robust data, while complete stack investigations are primarily necessary for validation purposes.
• Cyclic stress tests work at both levels, although a thorough examination of the test bench infrastructure is necessary in advance.
• Stack test benches are technically valuable for characterisation work, but very cost-intensive for detailed degradation analysis.
The results show: with the right methodological approach, the development of forward-looking PEM electrolysis technologies can be made significantly more efficient, representing an important step towards sustainable hydrogen production.
Project coordination
Rebekka Köll
Konsortialführung
HyCentA Research GmbH
T +43 (0) 316 873 9480
koell@hycenta.at
HyTechonomy
HyCentA Research GmbH
Inffeldgasse 15
8010 Graz
T +43 (0) 316 873 9500
office@hycenta.at
Project partner
- AIT, AUT
- AVL, AUT
- BEST Research, AUT
- Bosch, AUT
- Henn, AUT
- Profactor, AUT
- Postbus, AUT
- TU Graz (CEET, IWT, ITNA), AUT
- Verbund, AUT